在 JavaScript 中实现 MVC 和 PubSub
原文: https://howtodoinjava.com/javascript/implement-mvc-and-pubsub-in-javascript/
我们知道什么是 MVC? MVC 代表模型 - 视图 - 控制器。 简而言之,MVC 是一种设计技术,其中将应用组件分为 3 组,以便可以独立开发它们而无需考虑它们将如何交互。 如果构建正确,则很少有配置代码可以绑定它们,并且可以立即使用。
PubSub(发布者订阅者) 模型是设计范式,其中多个订阅者正在监听源上的更改事件,并且一旦发生任何更改,便会立即通知监听器。 在用户交互影响屏幕上多个部分的大型系统中,此模式消除了许多硬编码,并提供了设计灵活性。
JavaScript 中的 PubSub + MVC
在本教程中,我们将学习以下概念:
Building Model-View-Controller components
Building Publisher Subscriber infrastructure
Understanding Event Notification mechanism
Demo application
让我们从构建 MVC 组件开始。
构建模型视图控制器组件
在 JavaScript 中,如果必须开发 MVC 结构,则至少需要编写 3 个对象。 我只花 3 个使例子更加关注概念。
例如,我以媒体播放器为例。 此媒体播放器附有一个播放列表,用户可以使用按键事件在此播放列表上向前和向后移动。
模型:存储当前视图状态
playlist – 数组对象将所有曲目存储在当前可用的播放列表中。
currentIndex – 当前播放的曲目
模型还包含帮助用户在用户交互后保持其当前状态更改的函数。
var Model = {
playlist: new Array(),
currentIndex : 0,
reLoad: function() {
currentIndex = 0;
var tracks = document.getElementById("playListSelector").options;
for(var i=0; i<tracks.length; i++)
{
this.playlist[i] = tracks[i].value;
}
},
next: function () {
if(this.currentIndex < (this.playlist.length-1))
this.currentIndex++;
publish(this);
},
prev: function () {
if(this.currentIndex > 0)
this.currentIndex--;
publish(this);
},
current: function () {
publish(this);
}
};
视图:表示用户与之交互的屏幕
该对象只有一种方法可以在屏幕上呈现用户事件的结果。
var View = {
notify: function(model) {
document.getElementById("playListSelector").selectedIndex = model.currentIndex;
}
};
控制器:视图调用控制器以更改模型
控制器具有在用户交互期间将被调用的函数。
var Controller = {
model: Model,
moveNext: function () {
this.model.next();
return this;
},
movePrev: function () {
this.model.prev();
return this;
},
getCurrent: function () {
this.model.current();
return this;
}
};
构建发布者订阅服务器基础结构
到目前为止,一切都很好。 现在,我们将添加一些 pub-sub 逻辑,以便无论何时触发任何用户事件,都会通知所有已注册的视图,并且它们可以进行所需的视觉更改。
//All subscribers for a event
var subscribers = [];
function publish(event) {
for (i in subscribers) {
subscribers[i].notify(event);
}
};
上面的代码声明了一个数组,该数组可用于存储所有感兴趣的视图以将其自身注册为事件监听器。 每当任何事件作为用户交互触发时,都会通知他们该事件。
要将视图注册为事件监听器,将使用以下代码:
//Subscribe for updates
subscribers.push(View);
了解事件通知机制
事件处理按以下顺序执行:
视图触发事件 -> 控制器触发模型更新 -> 模型将通知发送到 pubsub -> pubsub 通知所有有关事件的视图,以便它们可以更新用户屏幕
在上面的代码段中,假设用户按下了播放列表中的下一首曲目。 这是控制流:
- 用户按下“下一首”按钮
- 控制器的
moveNext()方法调用 moveNext()触发模型的next()方法next()方法增加当前正在播放曲目的currentIndexnext()方法使用publish()方法发布事件publish()方法调用notify()方法是所有注册的订户- 视图
notify()方法根据模型的当前状态更新用户屏幕
这样,所有可能的事件都将从控制器处理到视图层。 最后,我们一直都处于模型的当前状态。
演示应用
我已经在一个文件中使用了上述所有代码段,并使用 HTML select元素进行了虚拟播放列表行为。 select的当前选定选项代表媒体播放器中当前播放的曲目。
让我们看一下完整的演示代码:
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8">
<script language="javascript">
// PubSub
var subscribers = [];
function publish(event) {
for (i in subscribers) {
subscribers[i].notify(event);
}
};
// MVC
var Model = {
playlist: new Array(),
currentIndex : 0,
reLoad: function() {
currentIndex = 0;
var tracks = document.getElementById("playListSelector").options;
for(var i=0; i<tracks.length; i++)
{
this.playlist[i] = tracks[i].value;
}
},
next: function () {
if(this.currentIndex < (this.playlist.length-1))
this.currentIndex++;
publish(this);
},
prev: function () {
if(this.currentIndex > 0)
this.currentIndex--;
publish(this);
},
current: function () {
publish(this);
}
};
var View = {
notify: function(model) {
document.getElementById("output").innerHTML = JSON.stringify(model);
document.getElementById("playListSelector").selectedIndex = model.currentIndex;
}
};
var Controller = {
model: Model,
moveNext: function () {
this.model.next();
return this;
},
movePrev: function () {
this.model.prev();
return this;
},
getCurrent: function () {
this.model.current();
return this;
}
};
subscribers.push(View); // Subscribe for updates
function initializeModel()
{
Model.reLoad();
}
</script>
</head>
<body onload="initializeModel()">
<input type="button" onclick="Controller.getCurrent();" value="Current Track">
<input type="button" onclick="Controller.moveNext();" value="Next Track">
<input type="button" onclick="Controller.movePrev();" value="Previous Track">
<select id="playListSelector" multiple readonly>
<option value="0">Track 1</option>
<option value="1">Track 2</option>
<option value="2">Track 3</option>
<option value="3">Track 4</option>
</select>
<span id="output" />
</body>
</html>
上面的代码还有另外一个方法initializeModel(),该方法用于在页面加载时使用播放列表项初始化模型对象。 现在,当我们按“下一个曲目”时,选择元素中的下一个选项被选中。 同样,按下“上一曲目”按钮,则在选择列表中选择了上一个选项。
您将看到如下运行代码:
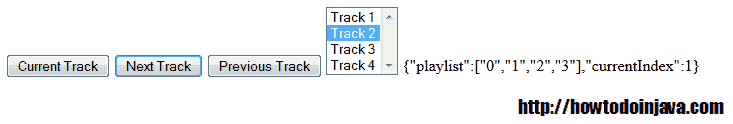
JavaScript 中的 MVC + PubSub 的示例界面
如果不清楚或您有任何建议/查询,请发表评论。
————————————————————————————————————
更新:
经过简短的邮件讨论后,Brook Monroe 向我发送了类似示例的更好的代码示例。 尽管本教程的目的不是更好的代码实践,而是详细介绍了概念。 我在下面共享更新的代码以供参考。 它可能会帮助您。
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8">
<script src="./pubsub.js"></script>
</head>
<body>
<button id="btnCurrent">Current Track</button>
<button id="btnNext">Next Track</button>
<button id="btnPrev">Previous Track</button>
<select id="playListSelector" multiple readonly>
<option value="0" selected>Track 1</option>
<option value="1">Track 2</option>
<option value="2">Track 3</option>
<option value="3">Track 4</option>
</select>
<span id="output"></span>
</body>
</html>
//pubsub.js
// PubSub
( function () {
"use strict";
var subscribers = [],
elCache = {},
Model = {
playlist : [],
currentIndex : 0,
reLoad : function()
{
var tracks = Array.prototype.slice.call(elCache.get("playListSelector").options);
this.playlist = [];
tracks.forEach( function (e,i) { this.playlist.push(tracks[i].value); }, Model);
this.currentIndex = 0;
},
next : function ()
{
if (this.currentIndex < (this.playlist.length-1)) {
this.currentIndex++;
}
subscribers.publish(this);
},
prev : function ()
{
if (this.currentIndex > 0) {
this.currentIndex--;
}
subscribers.publish(this);
},
current : function ()
{
subscribers.publish(this);
}
},
// MVC
View = {
notify : function(model)
{
elCache.get("output").innerHTML = JSON.stringify(model);
elCache.get("playListSelector").selectedIndex = model.currentIndex;
}
},
Controller = {
moveNext: function ()
{
Model.next();
return this;
},
movePrev: function ()
{
Model.prev();
return this;
},
getCurrent: function ()
{
Model.current();
return this;
}
};
function start()
{
elCache.get = function (elId)
{
return this[elId] || ( this[elId] = document.getElementById(elId) );
};
subscribers.publish = function (event)
{
this.forEach( function (e) { e.notify(event); } );
};
subscribers.push(View); // Subscribe for updates
elCache.get("btnCurrent").addEventListener("click", Controller.getCurrent.bind(Model));
elCache.get("btnNext").addEventListener("click", Controller.moveNext.bind(Model));
elCache.get("btnPrev").addEventListener("click", Controller.movePrev.bind(Model));
Model.reLoad.bind(Model)();
}
window.addEventListener("load",start,false);
} )();
祝您学习愉快!