使用 ETag 的 RESTEasy 缓存控制示例
原文: https://howtodoinjava.com/resteasy/jax-rs-resteasy-cache-control-with-etag-example/
ETags 或实体标签是很有用的 HTTP 标头,它们可以通过最小化系统上的服务器负载来帮助构建超快速的应用。 ETag 设置为对客户端的响应,因此客户端可以对条件请求使用各种控制请求标头,例如If-Match和If-None-Match。javax.ws.rs.core.Response.ResponseBuilder#tag()和javax.ws.rs.core.EntityTag是用于 ETag 的实用类。
在服务器端,不变的 ETag(HTTP 请求附带的 ETag 与为请求的资源计算的 ETag 之间的匹配)只是意味着,资源与上次请求时间相比没有变化,因此只需发送 HTTP 304 标头[未修改]就足够了, 客户端可以使用本地可用的资源副本而不必担心。
为了演示该示例,我在服务类中有两个 REST API。
a)GET http://localhost:8080/RESTEasyEtagDemo/user-service/users/1
此 API 将获取用户资源,该资源将附加有 ETag。 服务器将使用此 ETag 来验证用户详细信息是否已在上次请求中更新。
b)PUT http://localhost:8080/RESTEasyEtagDemo/user-service/users/1
此 API 将对服务器上的用户资源进行一些更新,这将强制服务器再次返回新的资源副本。
让我们逐步构建示例。
步骤 1)使用 maven 创建一个新的 Java Web 项目并添加以下依赖项。
<repositories>
<repository>
<id>jboss</id>
<url>http://repository.jboss.org/maven2</url>
</repository>
</repositories>
<dependencies>
<!-- core library -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.jboss.resteasy</groupId>
<artifactId>resteasy-jaxrs</artifactId>
<version>2.3.1.GA</version>
</dependency>
<!-- JAXB support -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.jboss.resteasy</groupId>
<artifactId>resteasy-jaxb-provider</artifactId>
<version>2.3.1.GA</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>net.sf.scannotation</groupId>
<artifactId>scannotation</artifactId>
<version>1.0.2</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
步骤 2)制作一个类来表示用户资源
确保提供一些逻辑来验证修改此资源后的最后更新时间。 我添加了一个日期类型为lastModied的字段。
package com.howtodoinjava.demo.rest.model;
import java.io.Serializable;
import java.util.Date;
import javax.xml.bind.annotation.XmlAccessType;
import javax.xml.bind.annotation.XmlAccessorType;
import javax.xml.bind.annotation.XmlAttribute;
import javax.xml.bind.annotation.XmlElement;
import javax.xml.bind.annotation.XmlRootElement;
@XmlAccessorType(XmlAccessType.NONE)
@XmlRootElement(name = "user")
public class User implements Serializable
{
@XmlAttribute(name = "id")
private int id;
@XmlAttribute(name="uri")
private String uri;
@XmlElement(name = "firstName")
private String firstName;
@XmlElement(name = "lastName")
private String lastName;
@XmlElement(name="last-modified")
private Date lastModified;
//Setters and Getters
步骤 3)在 DAO 层添加访问和修改资源的方法
我出于示例目的使用了静态HashMap。 在实时应用中,它将是一个数据库。 例如,我在映射中仅添加了一个用户。
package com.howtodoinjava.demo.rest.data;
import java.util.Date;
import java.util.HashMap;
import com.howtodoinjava.demo.rest.model.User;
public class UserDatabase
{
public static HashMap<Integer, User> users = new HashMap<Integer, User>();
static
{
User user = new User();
user.setId(1);
user.setFirstName("demo");
user.setLastName("user");
user.setUri("/user-management/users/1");
user.setLastModified(new Date());
users.put(1, user);
}
public static User getUserById(Integer id)
{
return users.get(id);
}
public static void updateUser(Integer id)
{
User user = users.get(id);
user.setLastModified(new Date());
}
public static Date getLastModifiedById(Integer id)
{
return users.get(id).getLastModified();
}
}
步骤 4)编写 Restful API 以访问和修改资源
这是主要步骤。 我已经在上面描述了两个 API。 GET API 返回附加了 ETag 的用户资源。 此 ETag 是在用户资源的最后修改日期计算的。 这将确保每次用户更新时,都会生成一个新的 ETag。
package com.howtodoinjava.demo.rest.service;
import javax.ws.rs.GET;
import javax.ws.rs.PUT;
import javax.ws.rs.Path;
import javax.ws.rs.PathParam;
import javax.ws.rs.core.CacheControl;
import javax.ws.rs.core.Context;
import javax.ws.rs.core.EntityTag;
import javax.ws.rs.core.Request;
import javax.ws.rs.core.Response;
import com.howtodoinjava.demo.rest.data.UserDatabase;
@Path("/user-service")
public class UserService
{
@GET
@Path("/users/{id}")
public Response getUserById(@PathParam("id") int id, @Context Request req)
{
//Create cache control header
CacheControl cc = new CacheControl();
//Set max age to one day
cc.setMaxAge(86400);
Response.ResponseBuilder rb = null;
//Calculate the ETag on last modified date of user resource
EntityTag etag = new EntityTag(UserDatabase.getLastModifiedById(id).hashCode()+"");
//Verify if it matched with etag available in http request
rb = req.evaluatePreconditions(etag);
//If ETag matches the rb will be non-null;
//Use the rb to return the response without any further processing
if (rb != null)
{
return rb.cacheControl(cc).tag(etag).build();
}
//If rb is null then either it is first time request; or resource is modified
//Get the updated representation and return with Etag attached to it
rb = Response.ok(UserDatabase.getUserById(id)).cacheControl(cc).tag(etag);
return rb.build();
}
@PUT
@Path("/users/{id}")
public Response updateUserById(@PathParam("id") int id)
{
//Update the User resource
UserDatabase.updateUser(id);
return Response.status(200).build();
}
}
警告:HTTP 标头中使用的日期的粒度不如数据源中使用的某些日期那么精确。 例如,数据库行中日期的精度可以定义为毫秒。 但是,HTTP 标头字段中的日期仅精确到秒。 在求值 HTTP 前提条件时,如果将java.util.Date对象直接与 HTTP 标头中的日期进行比较,则精度差异可能会产生意外结果。
为避免此问题,请使用日期对象的哈希码或使用某些规范化形式。
测试示例代码
1)首次请求:GET http://localhost:8080/RESTEasyEtagDemo/user-service/users/1
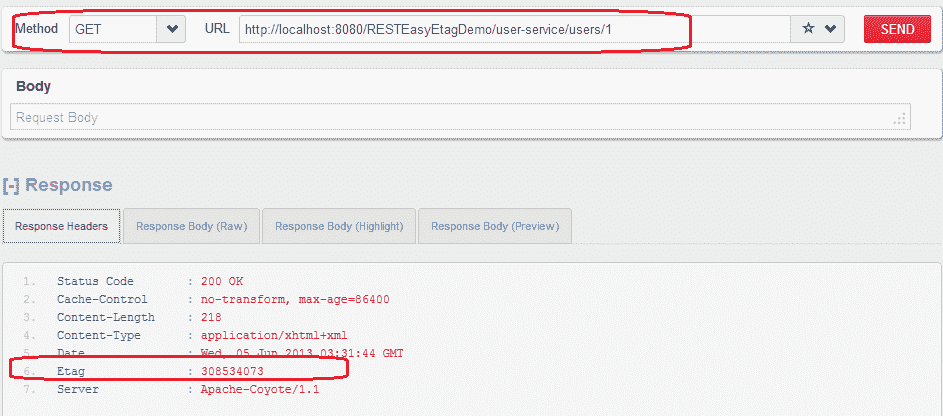
用户资源的第一次请求
2)后续请求:GET http://localhost:8080/RESTEasyEtagDemo/user-service/users/1
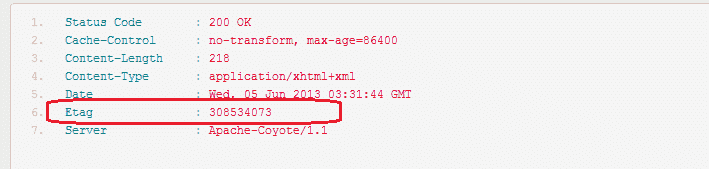
用户资源的后续请求
3)修改请求:PUT http://localhost:8080/RESTEasyEtagDemo/user-s:rvice/users/1
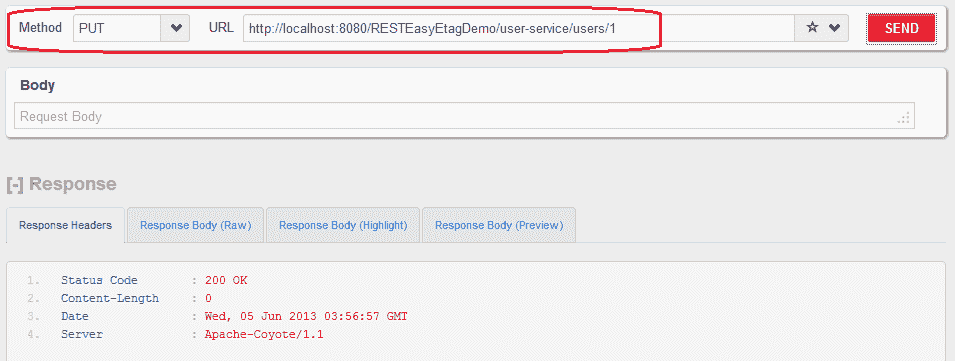
使用 PUT API 更新的用户资源
4)更新资源:GET http://localhost:8080/RESTEasyEtagDemo/user-service/users/1
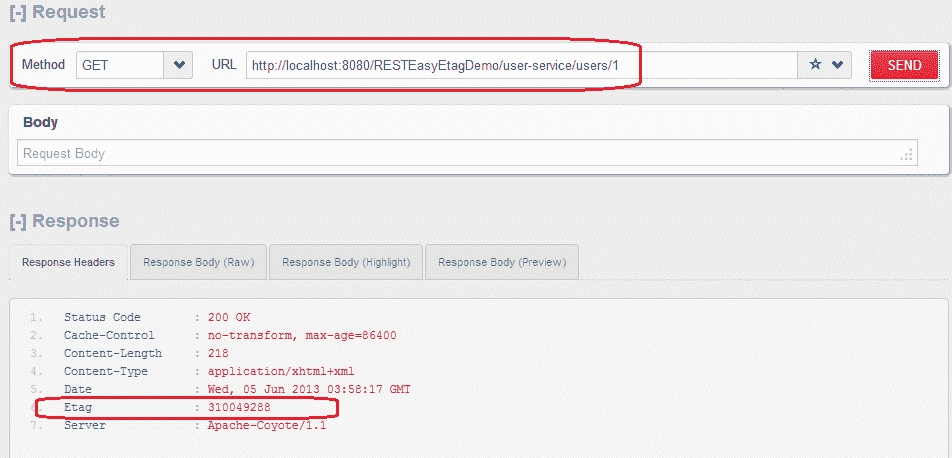
检索更新的用户资源
要下载以上示例的源代码,请单击下面给出的链接。
祝您学习愉快!