Java 读取 XML – Java DOM 解析器示例
原文: https://howtodoinjava.com/xml/read-xml-dom-parser-example/
在此 Java xml 解析器教程中,学习用 Java 中的 DOM 解析器读取 xml。 DOM 解析器旨在将 XML 作为内存中的对象图(树状结构)使用 – 称为“文档对象模型(DOM)”。
首先,解析器遍历输入的 XML 文件并创建与 XML 文件中的节点相对应的 DOM 对象。 这些 DOM 对象以树状结构链接在一起。 一旦解析器完成了解析过程,我们就会从中获得这种树状 DOM 对象结构。 现在,我们可以根据需要来回遍历 DOM 结构 - 从中获取/更新/删除数据。
Table of Contents
1\. DOM Parser API
-Import XML-related packages
-Create a DocumentBuilder
-Create a Document from a file or stream
-Validate Document structure
-Extract the root element
-Examine attributes
-Examine sub-elements
2\. Read XML with DOM parser
3\. Read data to POJO objects
4\. Parse "unknown" xml with DOM parser
阅读更多: DOM 解析器和 SAX 解析器之间的区别
出于示例目的,我们将在所有代码示例中解析 xml 内容。
<employees>
<employee id="111">
<firstName>Lokesh</firstName>
<lastName>Gupta</lastName>
<location>India</location>
</employee>
<employee id="222">
<firstName>Alex</firstName>
<lastName>Gussin</lastName>
<location>Russia</location>
</employee>
<employee id="333">
<firstName>David</firstName>
<lastName>Feezor</lastName>
<location>USA</location>
</employee>
</employees>
1. DOM 解析器 API
让我们记下一些主要步骤,以创建并使用 DOM 解析器来解析 Java 中的 XML 文件。
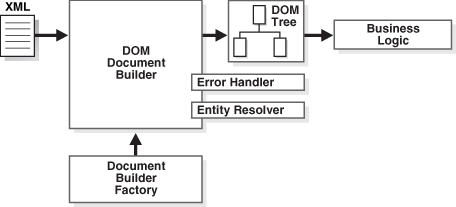
DOM 解析器的实际应用
1.1 导入 dom 解析器包
我们将需要首先在我们的应用中导入 dom 解析器包。
import org.w3c.dom.*;
import javax.xml.parsers.*;
import java.io.*;
1.2 创建DocumentBuilder
下一步是创建DocumentBuilder对象。
DocumentBuilderFactory factory = DocumentBuilderFactory.newInstance();
DocumentBuilder builder = factory.newDocumentBuilder();
1.3 从 xml 文件创建Document对象
将 XML 文件读取到Document对象。
Document document = builder.parse(new File( file ));
1.4 验证文件结构
XML 验证是可选的,但最好在开始解析之前进行验证。
Schema schema = null;
try {
String language = XMLConstants.W3C_XML_SCHEMA_NS_URI;
SchemaFactory factory = SchemaFactory.newInstance(language);
schema = factory.newSchema(new File(name));
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackStrace();
}
Validator validator = schema.newValidator();
validator.validate(new DOMSource(document));
1.5 提取根元素
我们可以使用以下代码从 XML 文档中获取根元素。
Element root = document.getDocumentElement();
1.6 检查属性
我们可以使用以下方法检查 xml 元素属性。
element.getAttribute("attributeName") ; //returns specific attribute
element.getAttributes(); //returns a Map (table) of names/values
1.7 检查子元素
子元素可以以下方式查询。
node.getElementsByTagName("subElementName") //returns a list of sub-elements of specified name
node.getChildNodes() //returns a list of all child nodes
2.使用 DOM 解析器读取 XML
在下面的示例代码中,我假设用户已经知道employees.xml文件的结构(它的节点和属性); 因此,示例直接开始获取信息并开始在控制台中打印信息。 在现实生活中的应用中,我们将这些信息用于某些实际目的,而不是在控制台上打印并离开。
//Get Document Builder
DocumentBuilderFactory factory = DocumentBuilderFactory.newInstance();
DocumentBuilder builder = factory.newDocumentBuilder();
//Build Document
Document document = builder.parse(new File("employees.xml"));
//Normalize the XML Structure; It's just too important !!
document.getDocumentElement().normalize();
//Here comes the root node
Element root = document.getDocumentElement();
System.out.println(root.getNodeName());
//Get all employees
NodeList nList = document.getElementsByTagName("employee");
System.out.println("============================");
for (int temp = 0; temp < nList.getLength(); temp++)
{
Node node = nList.item(temp);
System.out.println(""); //Just a separator
if (node.getNodeType() == Node.ELEMENT_NODE)
{
//Print each employee's detail
Element eElement = (Element) node;
System.out.println("Employee id : " + eElement.getAttribute("id"));
System.out.println("First Name : " + eElement.getElementsByTagName("firstName").item(0).getTextContent());
System.out.println("Last Name : " + eElement.getElementsByTagName("lastName").item(0).getTextContent());
System.out.println("Location : " + eElement.getElementsByTagName("location").item(0).getTextContent());
}
}
程序输出:
employees
============================
Employee id : 111
First Name : Lokesh
Last Name : Gupta
Location : India
Employee id : 222
First Name : Alex
Last Name : Gussin
Location : Russia
Employee id : 333
First Name : David
Last Name : Feezor
Location : USA
3.将数据读取到 POJO 对象
现实生活中另一个应用的要求可能是使用上面示例代码中提取的信息填充 DTO 对象。 我写了一个简单的程序来帮助您了解如何轻松完成它。
假设我们必须填充Employee对象,其定义如下。
public class Employee
{
private Integer id;
private String firstName;
private String lastName;
private String location;
//Setters and Getters
@Override
public String toString()
{
return "Employee [id=" + id + ", firstName=" + firstName + ", lastName=" + lastName + ", location=" + location + "]";
}
}
现在查看示例代码以填充员工对象列表。 就像在代码之间插入几行,然后将值复制到 DTO 而不是控制台中一样简单。
Java 程序,用于使用 DOM 解析器读取 XML 文件。
public class PopulateDTOExamplesWithParsedXML
{
public static void main(String[] args) throws ParserConfigurationException, SAXException, IOException
{
List<Employee> employees = parseEmployeesXML();
System.out.println(employees);
}
private static List<Employee> parseEmployeesXML() throws ParserConfigurationException, SAXException, IOException
{
//Initialize a list of employees
List<Employee> employees = new ArrayList<Employee>();
Employee employee = null;
DocumentBuilderFactory factory = DocumentBuilderFactory.newInstance();
DocumentBuilder builder = factory.newDocumentBuilder();
Document document = builder.parse(new File("employees.xml"));
document.getDocumentElement().normalize();
NodeList nList = document.getElementsByTagName("employee");
for (int temp = 0; temp < nList.getLength(); temp++)
{
Node node = nList.item(temp);
if (node.getNodeType() == Node.ELEMENT_NODE)
{
Element eElement = (Element) node;
//Create new Employee Object
employee = new Employee();
employee.setId(Integer.parseInt(eElement.getAttribute("id")));
employee.setFirstName(eElement.getElementsByTagName("firstName").item(0).getTextContent());
employee.setLastName(eElement.getElementsByTagName("lastName").item(0).getTextContent());
employee.setLocation(eElement.getElementsByTagName("location").item(0).getTextContent());
//Add Employee to list
employees.add(employee);
}
}
return employees;
}
}
程序输出。
[Employee [id=111, firstName=Lokesh, lastName=Gupta, location=India],
Employee [id=222, firstName=Alex, lastName=Gussin, location=Russia],
Employee [id=333, firstName=David, lastName=Feezor, location=USA]]
4.使用 DOM 解析器解析“未知” xml
上一个示例显示了在编写代码时,我们如何遍历具有已知或几乎不知道的结构的 XML 文档。 在某些情况下,我们可能必须以某种方式编写代码,以便即使在编码时假定的 XML 结构存在某些差异,程序也必须能够正常运行。
在这里,我们遍历 XML 文档树中存在的所有元素。 我们可以添加我们的知识并修改代码,以便在遍历树时只要获得所需信息,我们就可以使用它。
public class ParseUnknownXMLStructure
{
public static void main(String[] args) throws ParserConfigurationException, SAXException, IOException
{
//Get Document Builder
DocumentBuilderFactory factory = DocumentBuilderFactory.newInstance();
DocumentBuilder builder = factory.newDocumentBuilder();
//Build Document
Document document = builder.parse(new File("employees.xml"));
//Normalize the XML Structure; It's just too important !!
document.getDocumentElement().normalize();
//Here comes the root node
Element root = document.getDocumentElement();
System.out.println(root.getNodeName());
//Get all employees
NodeList nList = document.getElementsByTagName("employee");
System.out.println("============================");
visitChildNodes(nList);
}
//This function is called recursively
private static void visitChildNodes(NodeList nList)
{
for (int temp = 0; temp < nList.getLength(); temp++)
{
Node node = nList.item(temp);
if (node.getNodeType() == Node.ELEMENT_NODE)
{
System.out.println("Node Name = " + node.getNodeName() + "; Value = " + node.getTextContent());
//Check all attributes
if (node.hasAttributes()) {
// get attributes names and values
NamedNodeMap nodeMap = node.getAttributes();
for (int i = 0; i < nodeMap.getLength(); i++)
{
Node tempNode = nodeMap.item(i);
System.out.println("Attr name : " + tempNode.getNodeName()+ "; Value = " + tempNode.getNodeValue());
}
if (node.hasChildNodes()) {
//We got more childs; Let's visit them as well
visitChildNodes(node.getChildNodes());
}
}
}
}
}
}
程序输出:
employees
============================
Node Name = employee; Value =
Lokesh
Gupta
India
Attr name : id; Value = 111
Node Name = firstName; Value = Lokesh
Node Name = lastName; Value = Gupta
Node Name = location; Value = India
Node Name = employee; Value =
Alex
Gussin
Russia
Attr name : id; Value = 222
Node Name = firstName; Value = Alex
Node Name = lastName; Value = Gussin
Node Name = location; Value = Russia
Node Name = employee; Value =
David
Feezor
USA
Attr name : id; Value = 333
Node Name = firstName; Value = David
Node Name = lastName; Value = Feezor
Node Name = location; Value = USA
这就是 Java XML DOM 解析器的概念。 如果不清楚或需要更多说明,请给我评论。
学习愉快!
参考: